Global Biosimilars Market Size to reach USD 56.40 Billion by 2030 | CAGR 22.80 %.
Category: HealthcareThe Global Biosimilars Market Size was valued at USD 17.6 Billion in 2021, the market is projected to grow USD 56.40 Billion in 2030, at a CAGR of 22.80 %. as per the latest research report by Spherical Insights & Consulting.
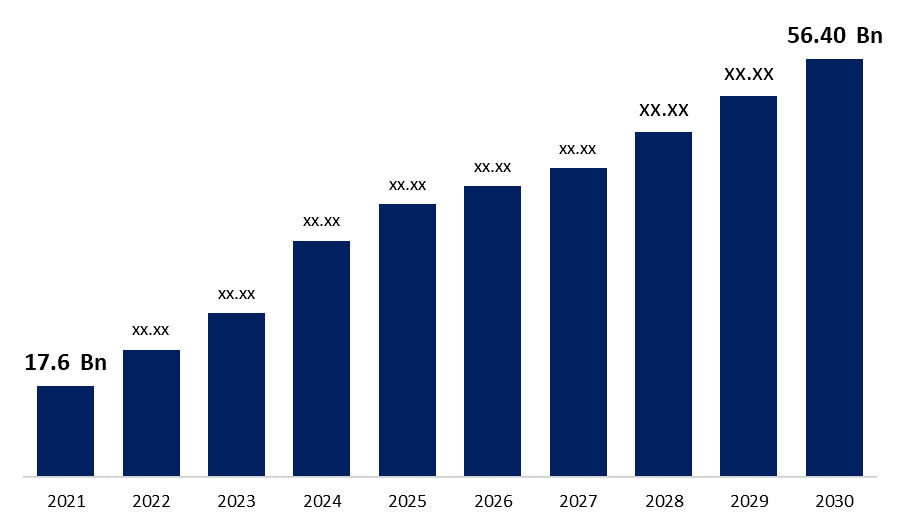
Get more details on this report -
Biosimilars are copy medications that are similar but not identical to biological drugs that have already been approved (the biological reference medicine). According to many nations' rules, a “similar biologic” is a biological product/drug created using genetic engineering techniques and claimed to be "similar" to a reference biologic in terms of safety, efficacy, and quality. Biosimilar medicine has an active ingredient that is similar to that of a biological reference medicine and is used to treat the same condition at the same dosage. Entity based (including product process), regulatory based (under expedited testing), and market based are all terms used to describe biosimilars (same manufactures, different trade name). Similar biological products, follow-up biologics, subsequent entry biologics, second entry biologics, biogenetics, multisource goods, and off patent biotech products are all synonyms for biosimilars. The general public and insurance companies prefer cost-effective options; however, the long-term economic implications of employing biosimilars have not been investigated. The entire cost of biosimilar therapy may increase.
Browse key industry insights spread across 196 pages with 119 market data tables and figures & charts from the report “Global Biosimilars Market Size, Share & Trends, COVID-19 Impact Analysis Report, By Product (Recombinant Human Growth Hormone (RHGH), Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor, Interferon, And Others), By Manufacturing Type (In-House Manufacturing, And Contract Manufacturing), By Technology (Recombinant DNA, And Monoclonal Antibodies), By Application (Offsite Treatment, Oncology, Chronic Disorder, Autoimmune Disease, And Others) And By Region (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East, And Africa), Analysis And Forecast 2021 – 2030” in detail along with the table of contents
https://www.sphericalinsights.com/reports/biosimilars-market
Biosimilars are a new class of medications that are designed to be safe and effective in the same way that off-patent biologicals are. Biologicals' active protein structure makes them more likely to elicit an acute and persistent immunological response. Biosimilars pose a low overall risk, but because of their structural complexity, manufacturing method, and immunogenicity risk, regulatory procedures are required.
The issues/limitations with biosimilars include that the two biosimilars may have different origins, may have the same therapeutic efficacy, and may have different adverse effects, necessitating extensive testing. The expiration of patent protection for many biological medications is the primary driver of biosimilar drug development. Because of the size and complexity of the active material, as well as the nature of the manufacturing process, biopharmaceuticals differ from traditional small molecule medications. Even minor change in the process can lead to the fatal outcome (process is product), safety, and efficacy issues.
The FDA's objective is to "guard the public's health by assuring the safety, efficacy, and security of human and veterinary medicines, biological products, and medical devices." The FDA carefully regulates biosimilar development, and each application is subjected to a comprehensive evaluation by the agency, which is based on separate but equally demanding requirements as its reference biologic. As a result, patients and prescribers can expect the same quality, safety, and efficacy as the reference biologic. While the development and regulatory assessment of a reference biologic is generally focused on Phase III clinical data, the development and evaluation of biosimilars is mostly focused on comparisons to the reference biologic that are most sensitive to detect differences.
Biosimilar development is fraught with complexity in terms of regulatory, manufacturing, and marketing, making it one of the most expensive development endeavors in the pharmaceutical industry. Biosimilars, like generic medications, are introduced to the market with the goal of lowering healthcare costs. However, biosimilar entrance entails higher costs, greater risks, and more time and expertise in terms of clinical development. Furthermore, biosimilars require a different marketing and launch approach than small-molecule generics. The significant costs of obtaining FDA clearance and developing manufacturing capacity will limit the number of biosimilar competitors.
In this situation, only a few biosimilar manufacturers are likely to try to enter the market for a specific innovator medication, and they are unlikely to offer their drugs at discounts of 10% to 30% of the innovator product's price. Furthermore, because there is no automatic substitution between a biosimilar and an originator product, the rate at which a biosimilar gains market share will be slower. As a result, it's simple to understand how the type and number of resources required for biosimilar research can create significant obstacles to entry, not just for small to mid-sized businesses, but also for bigger, well-established generics companies and multinational biopharmaceutical firms. 85–87 when there is no additional benefit above the innovator and only minor cost reductions, gaining market share for a biosimilar could be difficult. When numerous biosimilars are launched to the market, the price can be reduced.
Despite biosimilars' similarity to the innovator medicine, physicians and health care workers should be aware of some of the concerns that have arisen throughout the development and approval of these drugs, which highlight biosimilars' limitations. The use of biosimilars entails a shift in clinical practice. The Pan American and Health Education Foundation is actively interested in enhancing patient safety by playing a major role in educating patients and medical professionals about the dangers and benefits of biosimilars.
To ensure the safety, efficacy, and quality of biosimilar products, the FDA was given the ability to approve biosimilars, including interchangeable. The FDA is authorized to monitor a "abbreviated pathway" for approval of biologics that are "biosimilar" to already approved drugs under the Biologics Price Competition and Innovation Act of 2009. The shortened method will minimize needless and unethical biosimilar testing in both animals and humans. This will save time, money, and human resources. This is also supported by the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act of 2010 (USA). The introduction of biosimilars necessitates a carefully devised pharmacovigilance strategy.
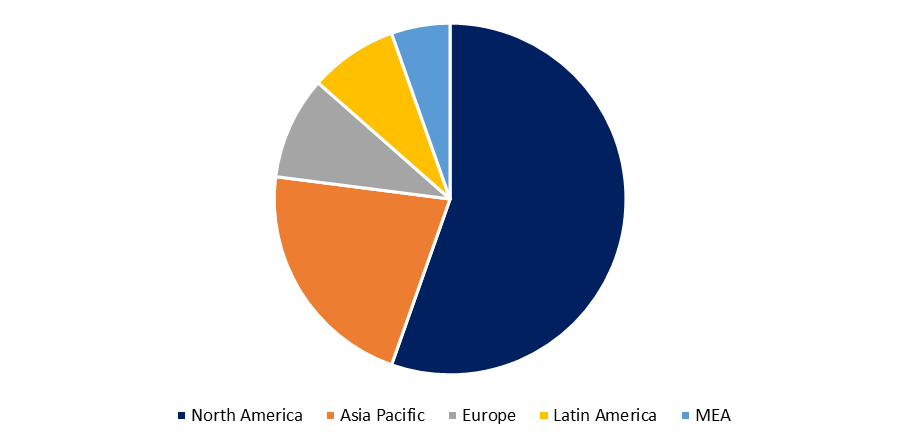
Biosimilars currently account for a major portion of the pharmaceutical market in the United States, Japan, and Europe since they are less expensive than biologic medications. Biosimilars, for example, are 30 percent less expensive than traditional biologic medications in Europe, where 21 have been approved. Only 18% of physicians, on the other hand, are aware of these same biologic pharmaceutical variances. Because 66 biologic U.S. patents expire between 2022 and 2030, the FDA expects to assess more biosimilar applications in 2021, the biosimilar business is on the verge of a big boost, cracking new markets. Furthermore, the patent cliff that these pharmaceuticals are facing will result in annual drug sales worth billions of dollars. Because the United States and Japan spend the most on biologics, they are expected to become the largest and most important biosimilar market centers. By 2021, off-patent pharmaceuticals are estimated to account for at least half of the market, offering a huge growth opportunity for biosimilars.
Get more details on this report -
The first biosimilar was approved in the United States in 2015, and with 12 biologic patents to expired in 2020, biosimilars are likely to take over the biologic business in a competitive manner. Furthermore, it is expected that biosimilars would account for 4% to 10% of the biologic market by 2021. The most successful US biosimilar to date (Zarxio) has captured over 55% of the filgrastim market in the United States (Hagen, 2020). Biosimilars, on the other hand, have had a slow acceptance in the United States. According to a new review of the largest US commercial health plans' biosimilar coverage decisions, only 14% of those decisions granted biosimilars preferential coverage (Chambers et al., 2020). While Europe is generally credited with considerably higher biosimilar uptake, up to 100% in some cases, its dominance in this sector is frequently exaggerated. While some European nations have a large biosimilar market share in particular therapeutic areas, biosimilar adoption varies widely across Europe and by product class (IQVIA, 2019b).
In 2018, 16 European nations used more than 90% of filgrastim and pegfilgrastim biosimilars, but just 27% of filgrastim and pegfilgrastim biosimilars were used in Ireland (IQVIA, 2019b). Norway and Denmark had the highest adoption of anti-tumor necrosis factor biosimilars (adalimumab, etanercept, and infliximab), with 81 percent and 96 percent, respectively, whereas every other country had less than 50 percent (IQVIA, 2019b).
Segmentation
By product
- Recombinant Human Growth Hormone (RHGH)
- Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor
- interferon
- others
By production type
- In-house manufacturing
- Contract Manufacturing
By Technology
- Recombinant DNA
- Monoclonal antibodies
By Application
- Off-site Processing
- Oncology
- Chronic diseases
- Autoimmune diseases
- others
By region
- North America – United States, Mexico, Canada
- Europe - UK, France, Germany, Italy, Spain and rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific – China, Japan, India, Korea and Rest of Asia Pacific
- South America - Brazil, Argentina, Colombia, Rest of South America
- Middle East and Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of Middle East and Africa
Related Report.
Global Nano Biosensors Market Size, Share & Trends, COVID-19 Impact Analysis Report, By Type (Nanoparticle-Based Sensors, Nanotube-Based Sensors, And Nanowire Based Sensors), By Product (Wearable Biosensors, And Non-Wearable Biosensors), By Industry Vertical (Healthcare, Consumer Electronics, Food & Beverage, Aerospace & Defense, And Others), And By Region (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East, And Africa), Analysis And Forecast 2021 – 2030
https://www.sphericalinsights.com/reports/nano-biosensors-market
Global Short-Acting Insulin Market Size, Share & Trends, COVID-19 Impact Analysis Report, Segmented by Drug (Apidra (Glulisine), Novolog/Novorapid, Humalog (Lispro), Novolin (Actrapid), Insuman, Humulin, FIASP, and Admelog) and Geography (North America, Europe, Latin America, Asia Pacific, and Middle-East and Africa) - Market Size Statistics & Forecasting To 2030
https://www.sphericalinsights.com/reports/short-acting-insulin-market
About the Spherical Insights & Consulting
Spherical Insights & Consulting is a market research and consulting firm which provides actionable market research study, quantitative forecasting and trends analysis provides forward-looking insight especially designed for decision makers and aids ROI.
Which is catering to different industry such as financial sectors, industrial sectors, government organizations, universities, non-profits and corporations. The company's mission is to work with businesses to achieve business objectives and maintain strategic improvements.
CONTACT US:
For More Information on Your Target Market, Please Contact Us Below:
Phone: +1 303 800 4326 (the U.S.)
Phone: +91 90289 24100 (APAC)
Email: inquiry@sphericalinsights.com, sales@sphericalinsights.com
Contact Us: https://www.sphericalinsights.com/contact-us
Need help to buy this report?