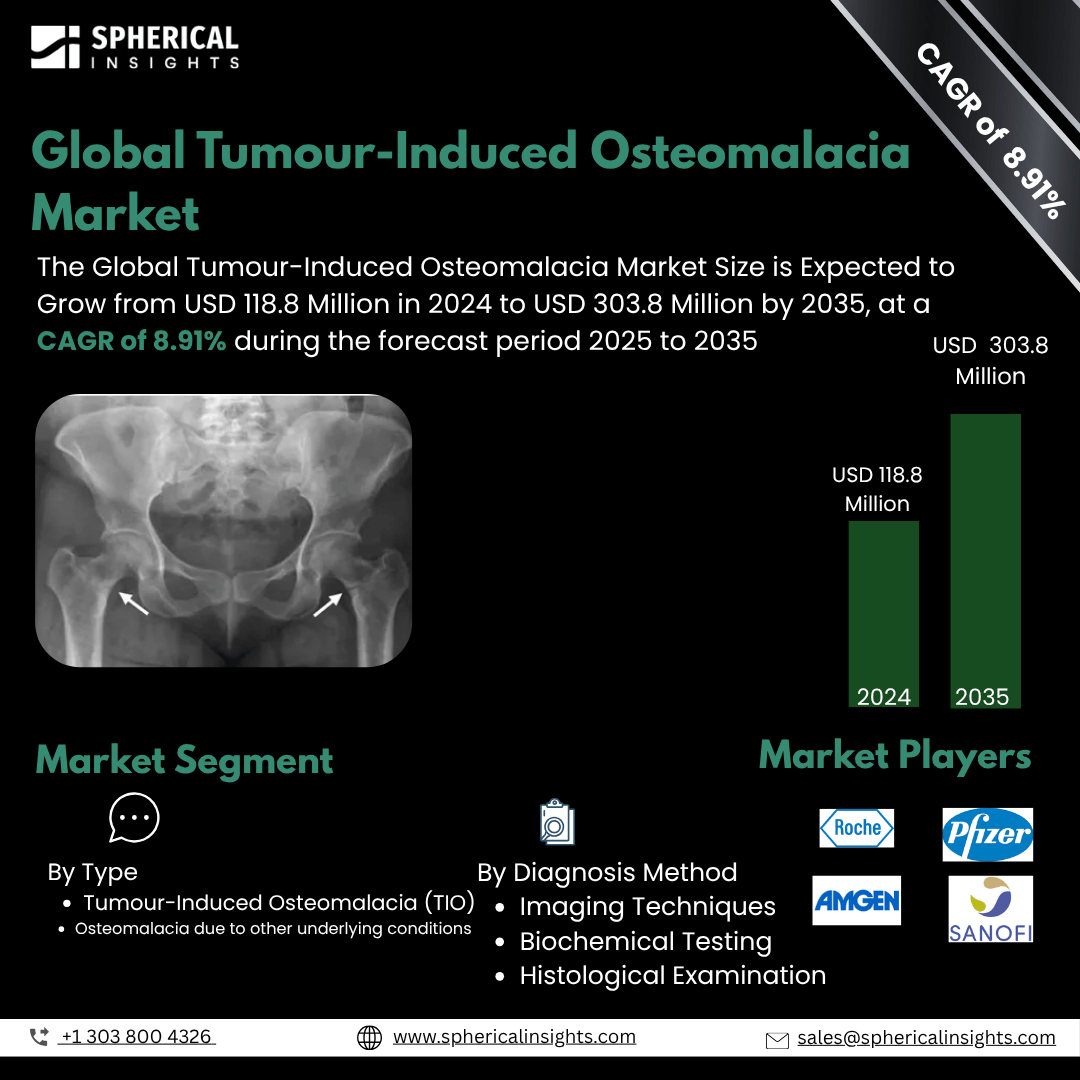
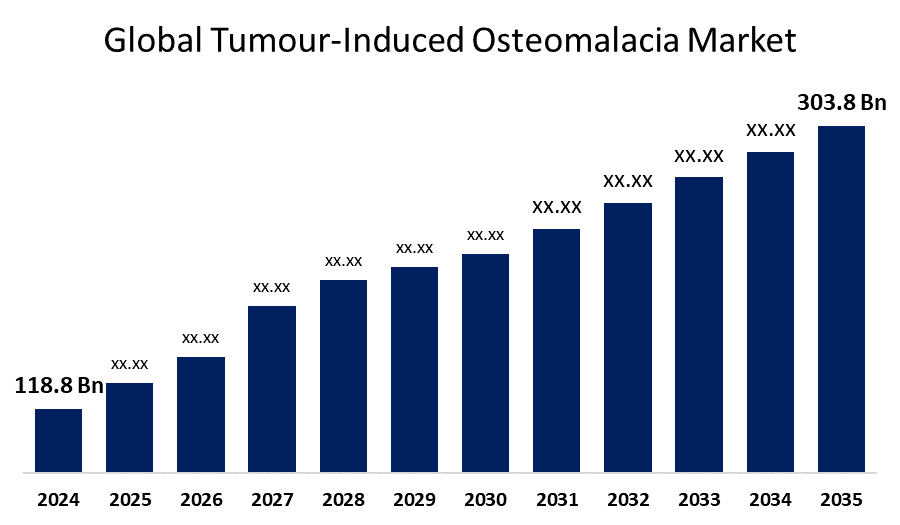
- As per Spherical Insights & Consulting, The Global Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia Market Size is Expected to Grow from USD 118.8 Million in 2024 to USD 303.8 Million by 2035, at a CAGR of 8.91% during the forecast period 2025 to 2035, owing to the launch of new therapies in the market and the rise in the number of cases.
- The leading Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia Market Companies such as Johnson & Johnson, Roche, Pfizer, Kyowa Kirin, Sanofi, Bayer AG, Merck & Co., GlaxoSmithKline, Amgen, Novartis, Eli Lilly, Teva Pharmaceuticals, Ultragenyx Pharmaceutical, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Abbott Laboratories, and Others.
Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia Treatment Market: Understanding and Treatment Algorithm:
Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia is a rare disorder caused by small, slow-growing tumors that secrete excess fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23), leading to phosphate loss and poor bone mineralization. It results in bone pain, fractures, and muscle weakness, often misdiagnosed due to its subtle symptoms and delayed tumor detection.
Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia Diagnosis:
Diagnosis of TIO involves identifying low phosphate levels, elevated FGF23, and increased alkaline phosphatase through blood tests. Advanced imaging techniques like PET-CT or MRI help localize the often hard-to-detect tumors. Biochemical testing is essential, and delayed diagnosis is common due to the tumor’s small size and rare occurrence.
Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia Treatment:
TIO treatment focuses on the surgical removal of the tumor, which often leads to full recovery. When surgery isn't possible, medications like phosphate supplements, calcitriol, and burosumab are used to manage symptoms and correct phosphate imbalance. Long-term follow-up is necessary to monitor recurrence and maintain bone health.
Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia Epidemiology:
The disease epidemiology covered in the report provides historical as well as forecasted epidemiology segmented by Total Diagnosed Incident Population of Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia, Gender specific Diagnosed Incidence of Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia, Type specific Diagnosed Incidence of Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia, Age specific Diagnosed Incidence of Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia, Diagnosed Incident Population based on Primary Site of Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia, and Diagnosed Incident Population based on Histologic Classification of Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia Tumour in the global market covering North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa from 2024 to 2035.
Principal Insights:
This section offers a global overview of Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia epidemiology in major markets worldwide.
Country Wise Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia Multiforme Epidemiology:
- The epidemiology segment provides Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia prevalence data and findings across key regions worldwide, including North America, Europe (Germany, France, Italy, Spain, and the United Kingdom), Asia-Pacific (including Japan), Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa.
Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia: Recent Developments:
- In August 2022, Kyowa Kirin announced that the European Commission had approved CRYSVITA (burosumab) for treating FGF23-related hypophosphatemia in Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia (TIO) associated with phosphaturic mesenchymal tumors that cannot be curatively resected or localized in children, adolescents, and adults.
Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia Marketed Drugs:
• Burosumab: Kyowa Kirin
Burosumab is a human monoclonal antibody that targets fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23), approved for X-linked hypophosphatemia and under expanded use for Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia. It works by inhibiting excess FGF23 activity, restoring phosphate levels, and improving bone mineralization. Burosumab offers a targeted treatment option for patients with FGF23-related phosphate-wasting disorders.
• Calcitriol: Abbott Laboratories
Calcitriol is the active form of vitamin D3 used to manage hypophosphatemia associated with TIO. It promotes calcium and phosphate absorption in the intestines and supports proper bone mineralization. Though not specific to TIO, it is commonly prescribed as part of supportive care in patients with phosphate-wasting disorders and osteomalacia.
Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia: Emerging Therapies:
- KRN23: It is also known as burosumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting FGF23, and is under investigation for treating Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia. It works by restoring phosphate levels and improving bone mineralization. Originally approved for X-linked hypophosphatemia, its application in TIO shows promise for patients unresponsive to conventional phosphate and vitamin D therapy.
- FGF23 siRNA: Its therapy is in early-stage development targeting overexpression of FGF23 in Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia. This small interfering RNA aims to silence FGF23 production at the genetic level, correcting phosphate wasting and promoting bone healing.
Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia Market Outlook:
- The Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia (TIO) market refers to the healthcare sector focused on diagnosing and treating a rare condition caused by FGF23-secreting tumors. It involves biochemical testing, imaging, and targeted therapies, including phosphate supplementation and monoclonal antibodies, aimed at correcting phosphate metabolism and restoring bone mineralization.
- Key market drivers include rising awareness of rare metabolic bone diseases, improved diagnostic technologies, and the availability of targeted therapies like burosumab. Growing patient registries, increased clinical research, and enhanced healthcare access in developing regions also support the expanding demand for effective TIO diagnosis and treatment.
- Opportunities lie in developing advanced biologics, expanding treatment accessibility in emerging markets, and enhancing early detection through novel biomarkers. Pharmaceutical investment in rare disease portfolios and increased collaboration between academia and biotech firms can further stimulate innovation in TIO-specific therapies and patient management strategies.
- Governments are promoting rare disease research through dedicated funding, orphan drug designations, and expedited regulatory pathways. Supportive policies in regions like the U.S. and EU help encourage clinical trials, improve diagnostics, and foster faster approval of innovative therapies for conditions like TIO.
- Limited awareness and delayed diagnosis remain major challenges due to the rarity and non-specific symptoms of TIO.
- The market is projected to grow steadily due to increasing adoption of targeted therapies and improved disease recognition.
Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia Market Segmentation:
By Type:
- Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia (TIO)
- Osteomalacia due to other underlying conditions
Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia (TIO) holds the largest market share due to the rarity and complexity of the condition, which drives specialized diagnostic and therapeutic demand. TIO often requires long-term care, surgical intervention, and targeted drug treatments, increasing healthcare expenditure per patient and contributing significantly to the overall market value compared to other osteomalacia forms.
By Diagnosis Method:
- Imaging Techniques
- Biochemical Testing
- Histological Examination
Biochemical Testing dominates the market as the primary diagnostic approach for TIO. It detects hallmark abnormalities like low phosphate levels and elevated FGF23, crucial for early and accurate diagnosis. Its non-invasive nature, affordability, and ability to guide further imaging or treatment make it the most widely adopted diagnostic method in clinical practice.
Regional Segment Analysis of the Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia Market:
North America leads the TIO market due to advanced diagnostic infrastructure, high awareness among clinicians, and early adoption of targeted therapies like burosumab. The region benefits from robust healthcare funding, active rare disease research programs, and strong regulatory support. Frequent clinical trials and patient registries further contribute to efficient disease management, enhancing regional market dominance in both diagnosis and treatment of TIO.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region in the TIO market, driven by increasing healthcare access, improving diagnostic capabilities, and growing awareness of rare bone disorders. Investments in healthcare infrastructure and government-led nutritional programs are improving early detection. Additionally, pharmaceutical companies are expanding their reach across emerging economies, creating new opportunities for TIO-specific treatments and long-term care innovations in this underserved patient population.
Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia Market Key Companies:
- Johnson & Johnson
- Roche
- Pfizer
- Kyowa Kirin
- Sanofi
- Bayer AG
- Merck & Co.
- GlaxoSmithKline
- Amgen
- Novartis
- Eli Lilly
- Teva Pharmaceuticals
- Ultragenyx Pharmaceutical
- Bristol-Myers Squibb
- Abbott Laboratories
- Others
Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia Therapeutics Market Report Scope:
- The Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia therapeutics market report provides a detailed overview, covering its causes, symptoms, disease progression, and existing treatment options.
- Detailed insights into Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia’s epidemiology and therapeutic approaches are included.
- Additionally, a comprehensive review of existing and emerging Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia therapies is provided, including an evaluation of new treatments expected to influence the current Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia treatment market landscape.
- The report includes a detailed review of the Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia therapeutics market, both historical and forecasted, highlighting the global drug reach.
- The Patient-Based Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia Market Forecasting report offers valuable insights into trends shaping the global Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia market, helping to develop effective business strategies.
Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia Treatment Market Report Insights:
- Forecasting Market Trends Based on Patient Data and Disease Rates
- Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia Therapeutic Approaches in Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia
- Review Of Drugs in Development for Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia
- Market, Growth, and Trends in Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia
- Market Opportunities in Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia Treatment
- Effects Of Future Therapies on Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia Treatment.
Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia Treatment Market Report Key Strengths
- 15 Years Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia Market Forecast
- Global Coverage
- Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia Epidemiology Segmentation
- Key Cross Competition
Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia Treatment Market Report Assessment
- Present Practices in the Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia Treatment Market
- Review of Investigational Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia Drugs
- Attractiveness of the Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia Drug Market
- Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia Market Drivers
- Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia Market Barriers
- SWOT
- Attribute Analysis
Market Segment:
This study forecasts revenue at the global, regional, and country levels from 2020 to 2035. Spherical Insights has segmented the Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia market based on the following segments:
Global Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia Market, By Type
- Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia (TIO)
- Osteomalacia due to other underlying conditions
Global Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia Market, By Diagnosis Method
- Imaging Techniques
- Biochemical Testing
- Histological Examination
Global Tumour-Induced Osteomalacia Market, By Regional Analysis
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- UK
- France
- Italy
- Spain
- Russia
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- Australia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- South America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of South America
- Middle East & Africa
- UAE
- Saudi Arabia
- Qatar
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East & Africa